


As legend has it, the evolution of karate began over a thousand years ago, possibly as early as the sixth Century A.D. when Bodhidharma arrived in Shaolin-si (small forest temple), China from India and taught Zen Buddhism. He also introduced a systematized set of exercises designed to strengthen the mind and body, exercises which allegedly marked the beginning of the Shaolin style of temple boxing. Bodhidharma’s teachings later became the basis for the majority of Chinese martial arts.
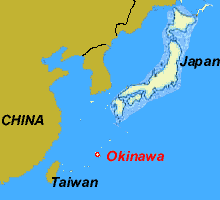

In its earliest stages, the martial art known as “karate” was an indigenous form of closed fist fighting which was developed in Okinawa and called Te, or ‘hand’. Okinawa had always experienced problems with rivals, but in 1429 the kingdoms were united and in order to maintain this unity, a decree was issued which banned possession of all weapons. This seemed to work well until 1609, when Okinawa was conquered by the rulers of the Satsuma Domain of Kyushu. Obviously, there was no incentive for the new rulers to permit the Okinawans to own weapons and they even put restrictions on their farming implements that could double as weapons. Without weapons for defense, the Okinawans were encouraged to develop the refinement of empty-hand techniques and, for this reason, Te was trained in secret



The Chinese character used to write Tode could also be pronounced ‘kara’ thus the name Te was replaced with kara te – jutsu or ‘Chinese hand art’ by the Okinawan Masters. This was later changed to karate-do by Gichin Funakoshi who adopted an alternate meaning for the Chinese character for kara, ’empty’. From this point on the term karate came to mean ’empty hand’. The Do in karate-do means ‘way’ or ‘path’, and is indicative of the discipline and philosophy of karate with moral and spiritual connotations.

No matter how you may excel in the art of te, And in your scholastic endeavors, Nothing is more important than your behavior
And your humanity as observed in daily life.


The brief meaning of Karate-do

INSTRUCTION AND ACHIEVEMENT
The language of karate-do is chiefly Japanese. A karate-do training hall or gym is called a dojo, and the white or black, pajama like garment worn in all training is called the Gi (Uniform). More than 200 specific Japanese terms are used for the various blows and moves that are employed in formal exercises called kata. A top karate-do instructor is known as a sensei. Most sensei must train for years to reach this level.
Degrees of achievement are formally recognized in Scorpion Karate-do training, each represented by a cloth belt of a particular color worn around the Gi (Uniform), the usual colors being, in ascending order, white, white yellow, yellow, green, green blue, blue, brown, red and black belt. Qualifications and colors for belts differ from school to school, depending upon the style and standard of karate-do taught.
The black belt, or Dan, signifies the highest proficiency in karate-do. Like the other belts the black belt is qualified by degrees of honor or skill, with 8th, 9th, or 10th being the highest Dan Black Belt that one can achieve depending on system. Currently, 8th Dan is the highest achieved in Scorpion Karate-do.
UNITED SCORPION KARATE-DO
The United Scorpion Karate-do Association (USKA) pledges itself to contributing to the art of Karate-do providing leadership and instruction in an ancient discipline that represents an alternative allowing practitioners to avoid the stresses and pitfalls of life in this modern age and by strengthening their minds and bodies. This mission will be undertaken within the guidelines of our tenets: Self-Control, Courage, Opportunity, Respect, Perseverance, Integrity, and Obviate.


